| Most Common Dental Problems | |
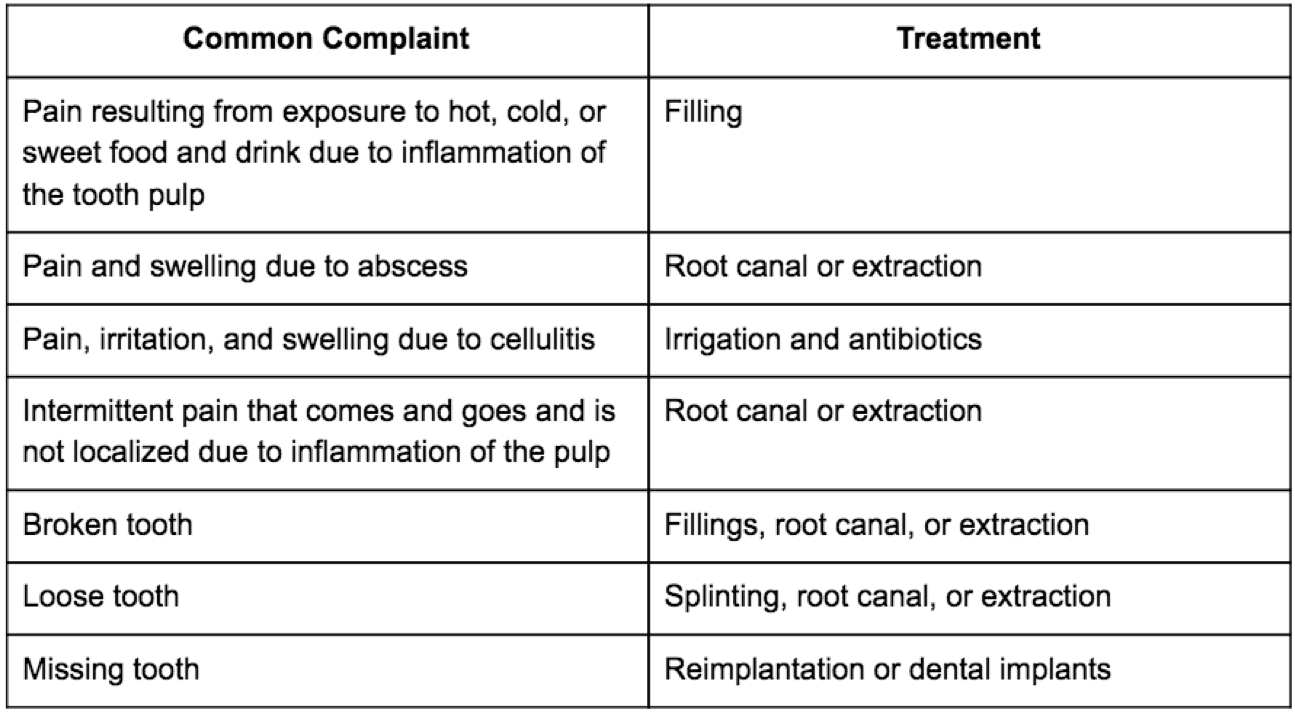
| Toothache | You’ve made a dentist appointment, and it can’t come soon enough. Meanwhile, it can help to rinse your mouth with warm water, floss to remove food caught between teeth, and take an over-the-counter pain reliever. If you notice swelling or pus around the tooth, or if you have a fever, that could be a sign that you have an abscess, a more serious problem. See your dentist as soon as possible. You may need antibiotics and possibly a root canal. |
| Stained Teeth | Your teeth are like your laundry: The right approach will remove many stains. Foods, medications, tobacco, and trauma are some of the things that can discolor your teeth. You have three options for whitening them. Your dentist can use a whitening agent and a special light. Or you can bleach them at home with a plastic tray and gel from your dentist or a store. The simplest choice, whitening toothpaste and whitening rinses, only remove surface stains. |
| Cavities / Tooth Decay | These little holes in your teeth are bad news. You get them when a sticky bacteria, called plaque, builds up on your teeth, slowly destroying the hard outer shell, called enamel. Adults can also have problems with tooth decay at the gum line and around the edges of earlier fillings. To prevent it, brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, limit snacks, floss daily, rinse with a fluoride mouthwash, and keep up with your dental appointments. Ask your dentist if you could benefit from a sealant. |
| Chipped Tooth | It’s the No. 1 type of dental injury. An accident can cause a chip. So can something much less dramatic, like chomping popcorn. Your dentist may recommend a crown if the chip is large or bonding with a strong resin material to replace the area that chipped. If the pulp is at risk, you may need a root canal followed by a veneer or crown. |
| Impacted Teeth | An adult tooth that doesn’t come in properly is “impacted.” It usually happens when a tooth is stuck against another tooth, bone, or soft tissue. If it isn’t bothering you, a dentist may recommend leaving it alone. But if it hurts or may cause problems later on, an oral surgeon can remove it. |
| Cracked Tooth | You were playing football without a mouth guard, or chewing, or maybe you don’t know how it happened, but now you’ve got a cracked molar. Can your dentist save the tooth? It depends. Most dentist recommend crowns for cracked teeth to prevent the crack from worsening. If the tooth is sensitive to hot and cold, the problem is more complex. Try to chew on the other side until you see your dentist. If the crack is above the gum line, you may need a root canal and a crown. A deeper crack means the tooth must be pulled, though. Fillings can increase the chance of a crack. |
| Tooth Sensitivity | Ice cream should taste good, not make you wince when the cold hits your teeth. The first step is to find the cause. It could be cavities, worn tooth enamel or fillings, gum disease, fractured teeth, or exposed roots. Once your dentist figures out the problem, you might need a filling, a root canal, or treatment of your gums to replace tissue lost at the root. Or you might just need a desensitizing toothpaste or strip, or a fluoride gel. |
| Too Many Teeth: Hyperdontia | How many teeth are in your mouth? If you’re like most people, you had 20 primary, or “baby,” teeth, and you now have 32 adult teeth. It’s rare, but some people have extra teeth, which is called hyperdontia. People who have it usually also have another condition, such as a cleft palate or Gardner’s Syndrome (which forms tumors that aren’t cancer). The treatment is to get the extra teeth removed and use orthodontics to correct the bite. |
| Crooked Teeth | The fix — orthodontia — isn’t just for kids. And straightening crooked teeth and aligning your bite doesn’t just make for a prettier smile. It can be an key part of improving overall dental health, relieving symptoms like jaw pain. Orthodontists may use braces (metal or trays), aligners, and retainers. |
| Jaw Pain or Soreness | Jaw pain can be a debilitating condition that affects your ability to eat and speak. Many things can cause jaw pain, from your sinuses and ears to your teeth or jaw itself. TMD also sometimes known as TMJ is the most common cause of jaw pain. The condition affects up to 12 percent of people. The temporomandibular joints are the hinge joints on each side of your jaw. Sometimes severe tooth infections known as dental abscesses can cause referred pain that radiates to the jaw. |